Dose Of Anti Tuberculosis Drugs In Renal Failure
-Patients 76 to 90 kg. 03102017 The International Union Against TB and Lung Disease in partnership with other institutions and agencies conducted the STREAM Evaluation of a Standardized Treatment Regimen of Anti-tuberculosis Drugs for Patients with Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis trial in multiple locations from across the world and evaluated the efficacy and safety of high-dose moxifloxacin.
 Ask Dis Anti Tuberculosis Drugs Renal Adjustment
Ask Dis Anti Tuberculosis Drugs Renal Adjustment
Out of a total of 37 anti-infective drugs 31 antibiotics 2 antivirals 4 antifungals 8 can be administered independent of renal function.

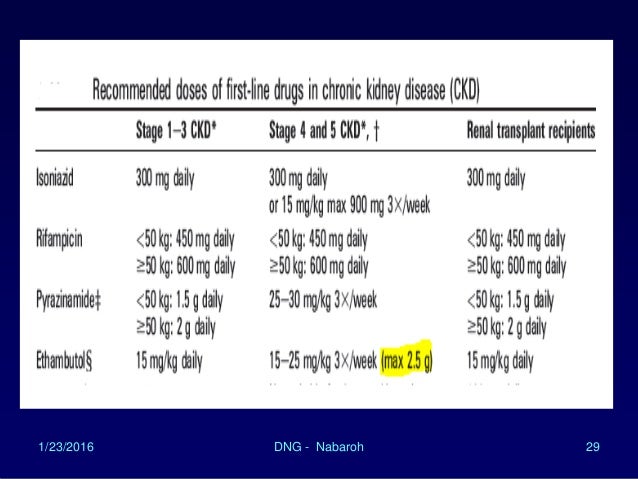
Dose of anti tuberculosis drugs in renal failure. People with kidney disease often only need very small doses of opioids and often get more side effects even with a small dose. 12-15 mgkg 2 or 3 times per week not daily Km a. Dose all once daily Adults.
22022021 3 times a week dosing recommendations. Side effects may include constipation feelingbeing sick. The symptomatology in renal patients is often insidious and nonspecific mimicking uremic symptoms whereas the localization is often extr.
25-5 mgkg per day. Tuberculosis and chronic renal disease. 1500 mg orally 3 times a week.
These medications are usually taken every four-six hours with a maximum of six doses in 24 hours. Breastfeeding renal failure or diabetes should additionally receive pyridoxine 10 mg daily. In a 12-month study of 572 CKD.
24102012 Teny Mathew John MD. Although about 27 of patients with AKI will have permanent renal impairment those who present with fever rash and GI disturbance at the onset of AKI have better renal recovery. In these individuals standard dosesmay be used but measurement of serum concentrations 2 and 6 hours post timed administration could be deployed to assist with optimizing drug dosages17 The commonly administered antitubercular drugs in patients of chronic renal failure CRF Maintenance HaemodialysisMHD and renal transplantation RT are isoniazid INH rifampicin.
15-25 mgkg 3 times per week not daily Rfb. 12-15 mgkg 2 or 3 times per week not daily Amk a. Thiocetazone should not be used.
Pyridoxin should be given with Isoniazid to prevent peripheral neuropathy if renal failure patients. In renal failure Isoniazid Rifampicin and Pyrazinamide can be given in normal doses. Dose and frequency if creatinine clearance.
16122015 Anti Tuberculosis Drugs. Q12h Use with significant caution in renal disease. There is an increased risk 69- to 525-fold of tuberculosis TB in patients with chronic renal failure and on dialysis as compared to the general population.
1 no adjustment in dosage and dose interval. Plasma level monitoring recommended but currently unavailable in Queensland. And 4 reduction of the dose and.
If the standard of health in the community is low pyridoxine should be offered routinely. 3 reduction of the dose without change in dose interval. It usually develops within two months of treatment and resolves within three months after onset.
However the efficacy and safety outcomes of such renal function-based dosage adjustments are. These tables summarize antiretroviral drug dosing recommendations for patients with impaired renal function. 15 mgkgday in a single daily dose 57 days per week maximum dose is generally 1 gram but a large muscular person could receive more and should have concentrations monitored.
In the presence of renal impairment anti-tuberculosis drugs can be modified by manipulating the dosage or dose interval or both as follows. First-line drug for the treatment of drug-susceptible tuberculosis. BID twice daily CrCl creatinine clearance HD hemodialysis PO orally by mouth Q2H Q4H etc every 2 hours every 4 hours etc.
Ethambutol was prescribed in seven cases. For established peripheral neuropathy pyridoxine should be given at a dose of 5075 mg daily. 01082002 Treatment was usually undertaken with a standard combination and doses of rifampicin isoniazid and pyrazinamide as per the BTS Guidelines 5 and was administered for 618 months in total.
The dose of isoniazid had been reduced in three cases to 200mg daily in two and 100mg daily in another. 13012014 Anti-tuberculosis drug-induced acute kidney injury is not rare in an aging population. For latent tuberculosis the standard treatment is six to nine months of daily isoniazid alone or three months of weekly 12 doses total of isoniazidrifapentine combination.
The following abbreviations are used throughout these tables. -Patients 56 to 75 kg. Main route of clearance is renal.
02052019 Dosages of anti-tuberculosis TB drugs are recommended to be adjusted according to renal function for patients complicated with chronic kidney disease CKD. 2 increase of the dose interval without decreasing dose. Renal Adjustment The recommended initial TB treatment regimen for patients with renal failure or severe renal insufficiency is 2 months of isoniazid rifampicin pyrazinamide and ethambutol followed by 4 months of isoniazid and rifampicin.
SAN DIEGOAnti-tuberculosis treatment ATT appears to be both safe and effective in patients with chronic kidney disease CKD data show. Patients with renal disease. 3000 mg orally 3 times a week.
2500 mg orally 3 times a week. 25 mgkg 3 times per week not daily E. For 29 anti-infective drugs a specific recommendation on drug dosage could be made in case of intermittent hemodialysis and for 24 anti-infective drugs in case of continuous hemodiafiltration.
Para-aminosalicylic Acid PAS 8-12gday in divided doses No dose adjustment required. -Patients 40 to 55 kg. 12-15 mgkg 2 or 3 times per week not daily Cm a.
Streptomycin and Ethambutol are avoided or given in low doses.
 Management Of Tb In Ckd Dr Tareq Tantawy
Management Of Tb In Ckd Dr Tareq Tantawy
 Ask Dis Anti Tuberculosis Drugs Renal Adjustment
Ask Dis Anti Tuberculosis Drugs Renal Adjustment
Comments
Post a Comment